As we all know, stainless steel is the abbreviation of stainless acid-resistant steel, which is resistant to air, steam, water and other weak corrosive media or steel grades with stainless steel, such as 201 (1Cr17Mn6Ni5N), 202 and other 2 series steel grades; The steel grades that are resistant to chemical corrosion media (acid, alkali, salt, etc.) become acid-resistant steel, such as 304 (06Cr19Ni10), 316 (0Cr17Ni12Mo2) and other 3 series steel grades.

Due to the difference in the chemical composition of the two, their ability to resist corrosion is different, like the 2 series stainless steel is generally not resistant to chemical corrosion, while the 3 series stainless steel has the ability to resist chemical corrosion.
Common labeling methods on the market include chemical formula (06Cr19Ni10), SUS (SUS304), of which 06Cr19Ni10 generally indicates national standard production, 304 generally represents United States ASTM standard production, and SUS 304 represents Japanese standard production.
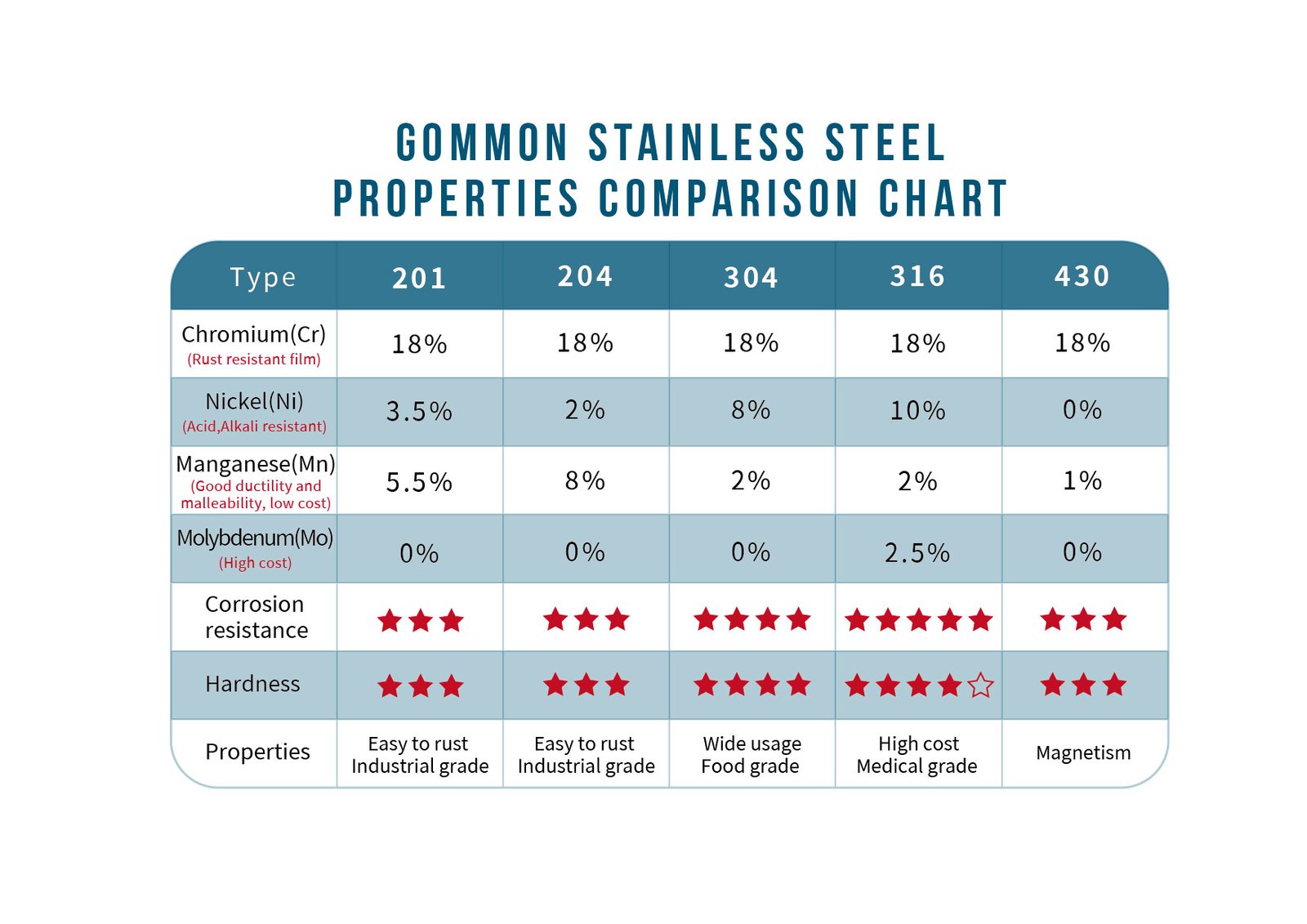
Of course, stainless steel is not completely rusty, but it has better corrosion resistance than ordinary steel, even if it is the same stainless steel, the corrosion resistance is also very different, such as 2 series and 3 series is obvious.
Sometimes we get a material, it is difficult to distinguish whether the material is 2 series or 3 series before the long-term environmental test, there are many detection methods on the market, briefly introduce two simpler methods, one is to look at the appearance, 201 as the representative of the 2 series contains high carbon and manganese, the surface will be darker, even if polished, it will be black and bright; The second is to look at the cutting sparks, the 201 material is relatively hard, and the sparks will be more but not larger when cutting;On the other hand, the 3 series represented by the 304 will be brighter, the texture will be relatively soft, and the cutting spark will be much smaller.
Stainless steel is closely related to our lives, the largest amount is 201 and 304, 316 quality is higher, 304 and 316 are stainless acid-resistant steel, both are sanitary stainless steel, suitable for use in coastal areas, but when the use of the environment chlorine content is relatively high, it is recommended to use 316, because 304 anti-corrosion is mainly the surface form of chromium oxide layer, that is, the blunt layer, when the chlorine content in the environment is relatively high, it will corrode the chromium oxide layer, so as to achieve the purpose of corroding the matrix, but 316 stainless steel contains molybdenum element, The addition of molybdenum gives it a special corrosion-resistant structure.
304 and 316 are both sanitary grade stainless steels, and there is no obvious difference in daily use 201, 304, and 316 are austenitic stainless steels, which are non-magnetic, and some are weak magnetic because of the appearance of a small amount of martensite or ferrite in the austenite due to component segregation or improper heat treatment during smelting.
The corrosion resistance of austenitic stainless steels comes from the chromium oxide protective layer formed on the surface of the metal. When the temperature of the material is heated to 450-900 degrees, the structure changes, and chromium carbide will be formed along the edge of the crystal instead of the chromium oxide protective layer, so that the corrosion resistance will be reduced, which is also called “intergranular corrosion”. As a result, 304L and 316L are available, both of which have less carbon content and less intergranular corrosion. In particular, a higher susceptibility to intergranular corrosion does not mean that non-low-carbon content is more susceptible to corrosion